Liquid Biopsy
ONCOCELL
Early detection is the best option.
OncoCell® is an analysis of blood samples used for the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in patients with or suspected of cancer, using the RT q-PCR technique.
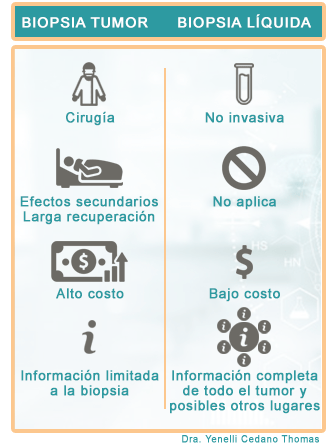
The OncoCell® test is completely safe, requires only a blood sample, is low risk, and has repeatability compared to other methods where tissue biopsies are used and require surgical intervention.
The OncoCell® analysis makes possible to quantify specific biomarkers of circulating tumor cells (characteristic sign of a metastasis process) using the reference to obtain patient results.
Do you know the benefits?
¡We invite you to read all the information about OncoCell®!
Importance of OncoCell®
OncoCell® is an analysis of blood samples that is used for the detection of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC’s) in patients with or suspected cancer, using the RT q-PCR technique. This test is totally safe since it only requires a simple extraction of peripheral blood and, in addition, this can be performed on repeated occasions to monitor and control the therapy of an oncological process.
The OncoCell® analysis allows the quantification of specific biomarkers of CTC’s in contrast to data from healthy patients.
The presence of CTC’s is a characteristic sign of cancer metastasis.
Timely monitoring
Early detection of cancer is key to ensuring a better outcome from cancer therapy for patients. In general, the first indication of suffering an oncological process is due to the manifestation of symptoms, such as; bleeding, lumps or wounds that do not heal, among others, other than the result of proactive tests.
Since these symptoms are sometimes ignored or erroneously related to other pathologies, many patients are diagnosed with cancer only at a more advanced stage, this makes treatment and recovery difficult for the patient.
Metastasis during an oncological process represents 90% of deaths from cancer compared to deaths from a primary tumor process. Therefore, it is essential to know as soon as possible about the presence or spread of cancer.
In patients who have been detected with a cancerous tumor, the OncoCell® analysis can be used to identify the presence of cancer and / or the metastatic process. This ensures that the knowledge of the presence of cancer is in the earliest possible stage and can lead to better therapeutic results.
In addition, continuous monitoring of the status of the cancer patient can be performed every 3 to 4 months, ensuring that any relapse is detected as soon as possible in order to find or select the most appropriate treatment for the patient; a regular test ensures peace of mind as early detection is the best option.
OncoCell test can detect cancer process faster than traditional tests.
What is the OncoCell® test?
Sampling

With a simple blood sample, the detection of an oncological process can be achieved, thanks to the technology of quantification of CTCs.
Analysis

Through the RT q-PCR method, the expression of specific tumor biomarkers associated with carcinomas is quantified.
Results

All the information regarding the analyzed markers, their expression levels, points of clinical interest and much more in your OncoCell® report.
If you decide to have the OncoCell® test, you will need to take into account several factors together with your doctor when deciding on your treatment. The information offered by this study has a high value for the choice of method.
The OncoCell® study will help you and your doctor to take best decisions.
Accurate and with greater advantages
The OncoCell® test is completely safe, requires only a blood sample, is low risk and has repeatability compared to other methods where they are used tissue biopsies and requiring surgical intervention. In addition, OncoCell® analysis has advantages over computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET), since these methods are invasive and with adverse side effects due to the introduction of the iodine-based contrast dye. which is the cause of vomiting, dizziness, headaches, among others … there are patients who CANNOT undergo these studies continuously due to side effects.
.
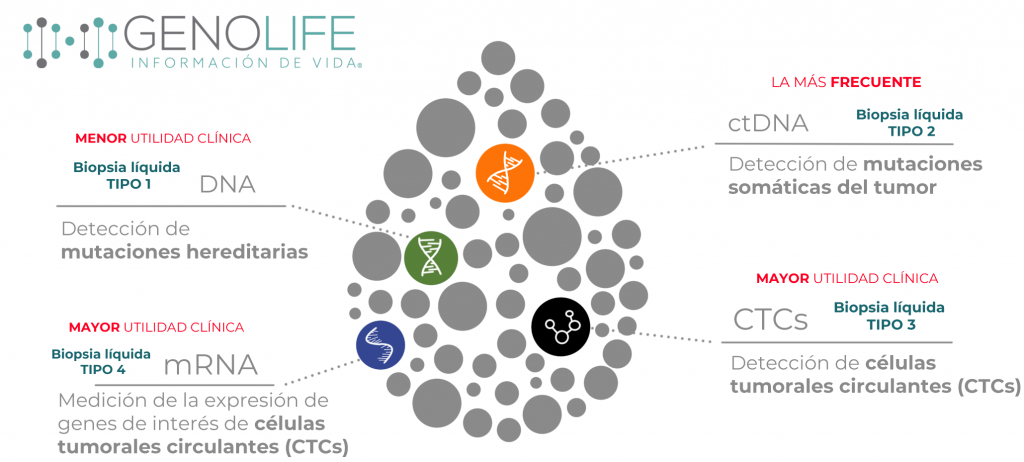
Liquid biopsy as a diagnostic technology
The liquid biopsy has been designed based on a theory based on tumor behavior, the genetic expression of biomarkers and the existence of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) as a detection method in early stages for better decision-making in the treatment of the patient. , assess the behavior of the condition according to the therapy used and periodically monitor the state to rule out possible relapses.
The gene expression profile that we offer at GENOLIFE includes more than 10 molecular biomarkers carefully selected by specialists, which have professional validation and supported by documentation from the scientific community.
This profile offers timely information to the oncologist for the appropriate treatment selection.
Molecular markers
|
|
Function |
|
Markers for the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs). |
|
|
Ep-CAM (EPCAM) |
Epithelial cell adhesion. Molecular marker used for the detection of CTC. |
|
E-CAD (CDH1) |
Epithelial cadherin (E-CAD) marker gene used for the detection of CTC |
|
CK-7 (KRT7) |
Cytokeratin 7. Marker for CTC detection. |
| CK-20 (KRT20) | Cytokeratin 20. Marker for CTC detection |
|
Markers for monitoring cell growth. |
|
|
Ki67 (MKI67) |
Cell growth factor. Prognostic marker used for breast cancer. |
|
EGFR (EGFR) |
EGF receiver. Growth marker present in breast, lung, colorectal cancer among others. |
| VEGF (VEGFA) | Growth factor that stimulates angiogenesis. |
|
Hormonal markers |
|
|
PGR (PGR) |
Progesterone receptor. Hormonal marker |
|
ER (ESR1) |
Estrogen receptor Hormonal marker |
| COX2 (PTGS2) | Cyclooxygenase-2 synthase of prostaglandin, promotes tumor progression, resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. |
| ALK (ALK) | Receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell multiplication, present in some types of cancer, such as neuroblastoma and non-small cell lung cancer. |
|
Targeted therapy markers |
|
|
CDKN2B (CDKN2B) |
Cell growth regulator. Associated with ovarian cancer. |
|
HER-2 (ERBB2) |
EGF receiver. Good diagnostic marker for breast, ovarian, lung, prostate, stomach and bowel cancer. |
|
PDL1 (CD274) |
Suppression of the immune system. The high tumor expression of PDL1 is associated with greater tumor aggressiveness. |
Improve your forecast with better tracking
What are CTCs?
Circulating tumor cells (CTC) are tumor cells that have been shed from a primary tumor and transported around the body through the bloodstream.
CTCs are seeds for further growth of additional tumors (metastases) in distant organs.
Why analyze them?
Modern cancer research has shown that CTCs are derived from clones in the primary tumor.
Tissue biopsies are poor diagnostic procedures: they are invasive, they can not be used repeatedly, and they are not effective in understanding metastatic risk, the progression of the disease, and the effectiveness of treatment.
How are CTCs analyzed?
CTCs can be identified because it is possible to quantify the expression of specific genes (molecular markers) such as the EpCAM (epithelial cell adhesion protein) gene that is expressed mostly in CTCs.
On the other hand there are other genes that are used as molecular markers to identify the presence of CTCs such as cytokeratins, including CK8, CK20 and specific tumor markers (PSA, HER-2, etc.).
What technique is used?
The technique used for the quantification of CTCs is the qPCR or real-time PCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction in English real time PCR)

What is analyzed?
In the total liquid biopsy of genolife, it quantifies the markers for the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs), such as EpCAM, E-CAD, CK-7 and CK20. Markers for cell growth monitoring (Ki67, EGFR, VEGF). Hormonal markers (PGR, ER, COX2) and markers of targeted therapies (CDKN2B, PDL1 and HER-2)
What kind of information do you receive?
The result of this analysis takes 5 business days after receiving the sample. The information of the liquid biopsy provides additional information to the attending physician about the patient’s cellular behavior